Table of Contents
IP Addresses
Obviously, IP Address objects in TeemIp modelize addresses of the Internet Protocol. Both version 4 and version 6 are supported.
IP Address Properties
| Name | Type | Mandatory? |
|---|---|---|
| General Information | ||
| Organization | Foreign key to a(n) Organization | Yes |
| Status | Possible values: allocated, released, reserved, unassigned | Yes |
| Usage | Foreign key to a(n) IP Address Usage | No |
| Note | Multiline character string | No |
| Requestor | Foreign key to a(n) Person | No |
| Allocation date | Date (year-month-day) | No |
| Release date | Date (year-month-day) | No |
| DNS Information | ||
| Short Name | Alphanumeric string | No |
| DNS Domain | Foreign key to a(n) Domain | No |
| DNS View | Foreign key to a(n) View Brought by the DNS Zone Management extension | No |
| FQDN | Alphanumeric string | No |
| Aliases | Array of alphanumeric strings | No |
| IP Information | ||
| Subnet | Foreign key to a(n) Subnet | No |
| Range | Foreign key to a(n) IP Range | No |
| Address | Alphanumeric string | Yes |
| Discovery Information | ||
| Set of attributes brought by the IP Discovery Data model extension | ||
- Allocated: IP is in use and potentially attached to a CI or an interface. It cannot be attached to another CI without being released or unassigned first unless the IP Setting Allow attachement of already allocated IPs to CIs is set to Yes.
- Released: IP is not in use anymore and doesn't ping. It and can be re-allocated or reserved if required
- Reserved: IP is not in use yet but will be allocated (activated) at a point in time. It can be allocated from the IP detail menu but is invisible from the CI edition menu.
- Unassigned: IP exists and pings but it is not attached to a CI or an interface. It can be allocated or reserved.
If IP Discovery Datamodel extension is installed, versions 3.2.0 and above bring the additional status Discovered to the IPObject class and therefore to the IP Addresses. This value may be set by the IP Discovery Data collector to newly discovered IPs and changed afterwards by the Hostmaster.
Tabs
| Tab | Description |
|---|---|
| Contacts | All the contacts for this IP |
| Documents | All the documents linked to this IP |
| Notifications | List of related notifications - Present if a notification trigger exists for that class |
| NAT IPs | All other IPs linked to this IP in a NAT relationship |
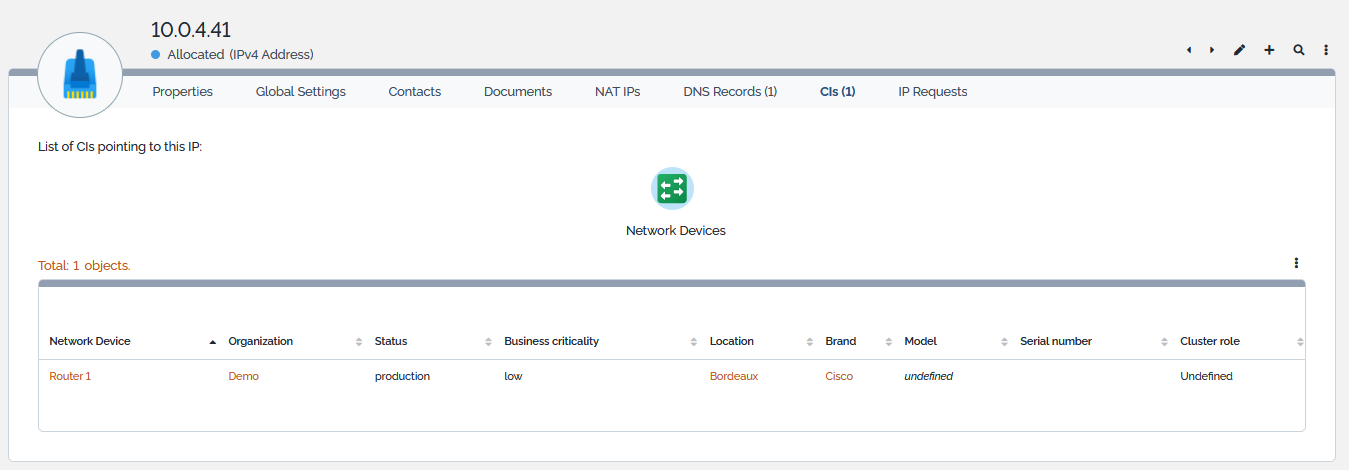
| CIs | All the configuration items configured with the IP |
| Activity panel | History of all changes made to the IP |
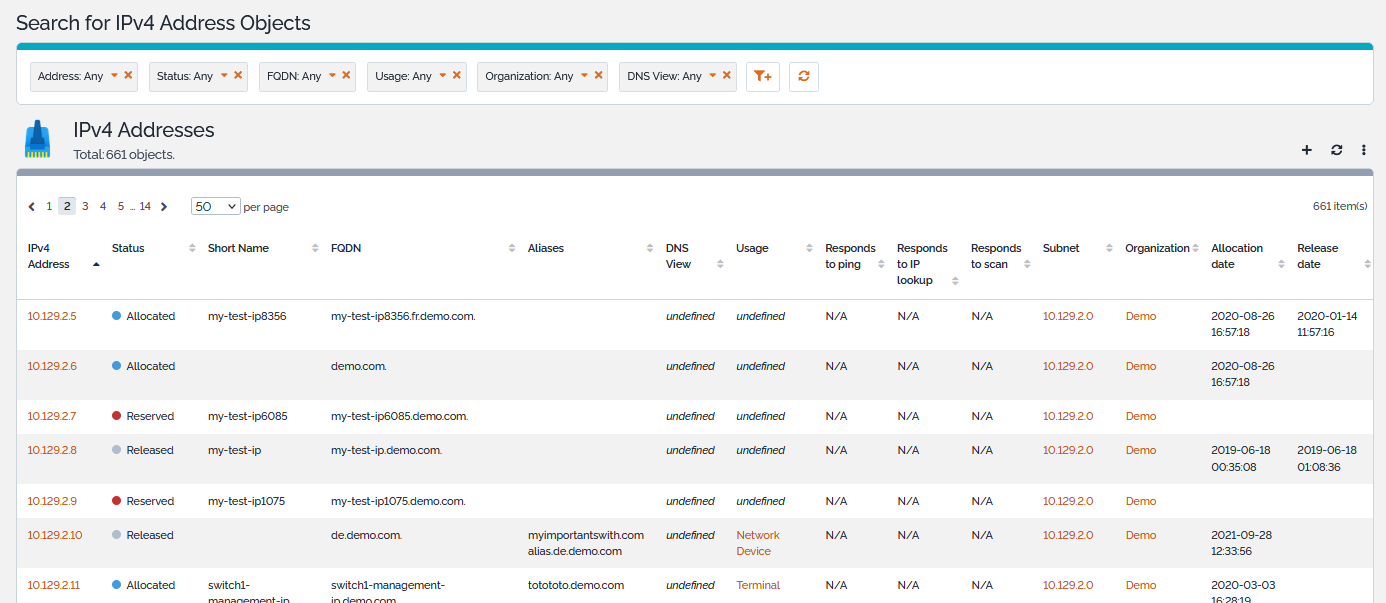
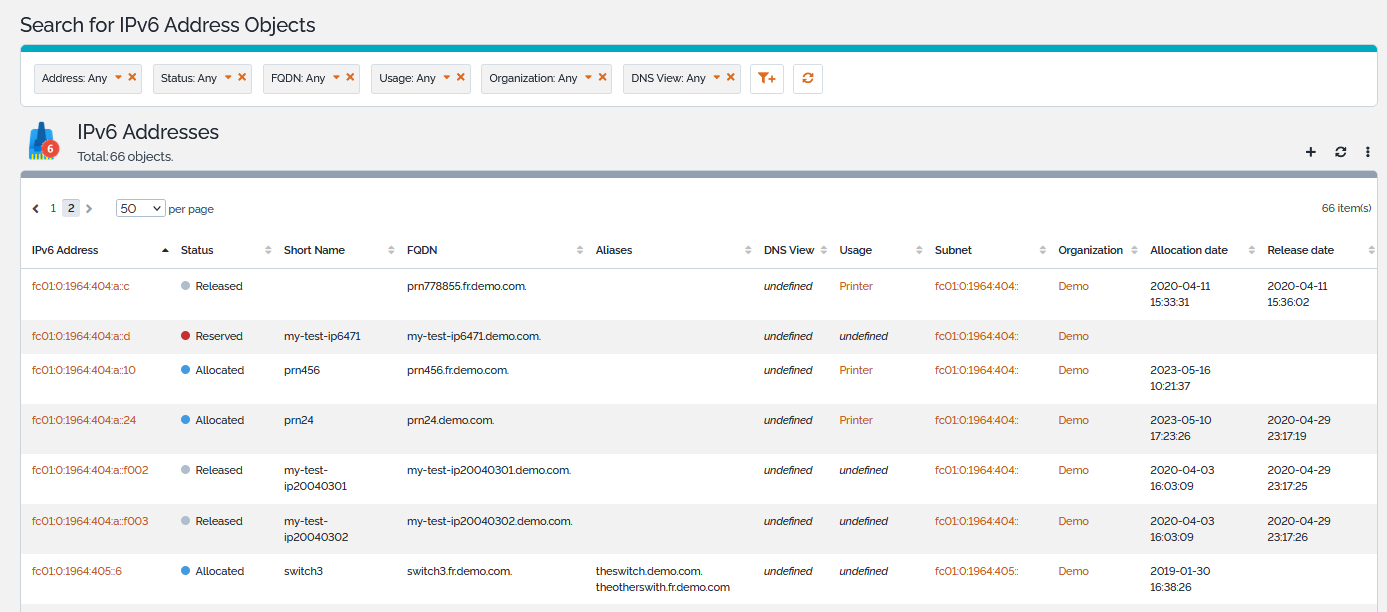
Listing IP Addresses
The IP Addresses shortcuts of the IP Management module on the explorer menu display all the IPv4 or IPv6 Addresses of the selected organization or all IPv4 or IPv6 Addresses if no organization is selected.
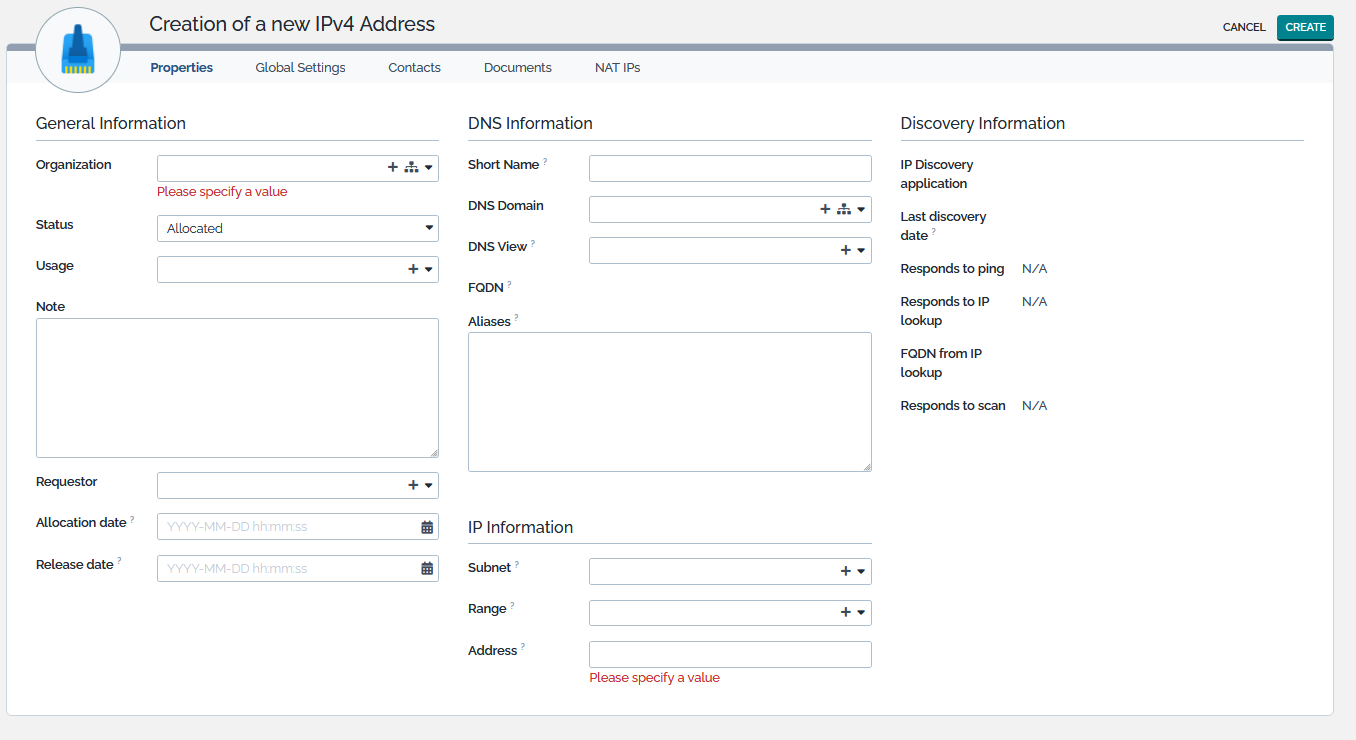
Creating a new IP Address
From the listing view or from any create action of an IP Address badge, click on the  to display the creation form.
to display the creation form.
An implicit but intuitive set of rules are followed when an IP address is created:
- Allocation date and FQDN (Fully Qualified Defined Name) are automatically calculated when the address is created,
- If no Subnet is selected, the IP can be any IP of the IPv4 (or IPv6) space,
- If a Subnet and no Range are selected, the address must be included into the Subnet,
- If a Subnet and a Range are selected, the address must be included into the Range as well,
- When attached to a CI, the Short Name is computed according to a method defined, by default, at the FunctionalCI level - see CMDB Core chapter,
- An IP can be linked to any other registered IP address through the NAT tab.
According to configuration parameter Allow Duplicate Names, unicity of the FQDN is checked:
- Duplicates may exist in different organizations,
- Within an organization, duplicates may exist in different DNS views,
- If parameter is set to:
- No, all other cases of duplicates are rejected,
- Dual stack, duplicates may exist between IPv4 and IPv6 spaces,
- Yes, unicity of FQDN is not verified.
According to configuration parameter Compute FQDN when short name is empty, the FQDN may be computed regardless the content of the Short Name and DNS Domain.
At creation time, global settings Allow Duplicate Names and Ping IP before assigning it can be overwritten. Note that a change on these parameters, if any, only applies to the current creation and don’t affect the value of the global parameters. If it is required to change them globally, these can be changed through the Global IP Settings menu of the Data Administration module.
Modifying an IP Address
From the detailed view of an IP Address, click on the ![]() button.
button.
Basically, all parameters can be changed here but, of course, the IP address itself.
Navigating between adjacent IPs
TeemIp provides an easy and efficient way to navigate between adjacent IPs. If the action is enabled, the left and rights arrows of the object menu ![]() will bring you to the previous or next registered IP in TeemIp. This action is driven by default parameters that can be overwritten in the configuration file.
will bring you to the previous or next registered IP in TeemIp. This action is driven by default parameters that can be overwritten in the configuration file.
'teemip-ip-mgmt' => array (
...
'ip_navigation' => array (
'enabled' => true,
'within_subnet_only' => false,
),
...
),
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| enabled | Enable or disable the function |
| within_subnet_only | Limit the navigation to the subnet that the IP belongs to or not |
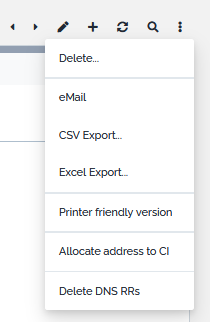
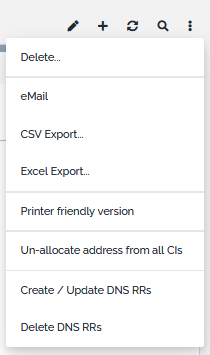
Other Actions
Next to standard actions, a set of specific actions can be applied to IP Addresses. These can be found in the Other Actions menu available from the details page.
These specific actions are described in below chapters.
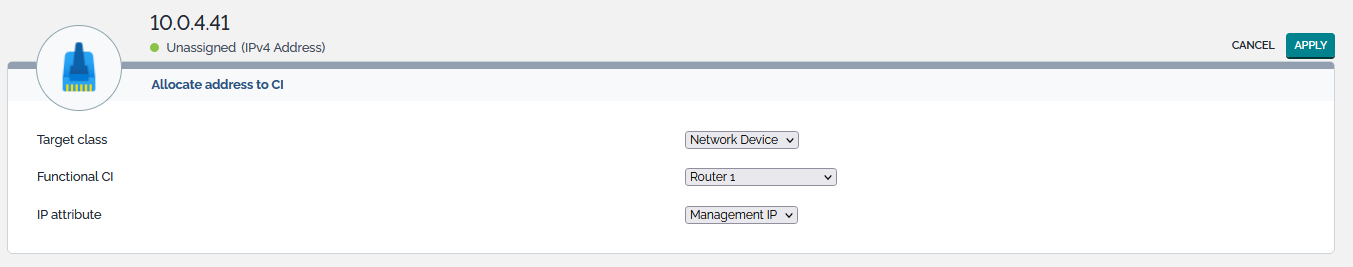
Allocate address to CI
This action applies to IP Addresses that are released, reserved or unassigned. Its purpose is to allocate the address to a CI without having to open the modification form of the targeted CI.
Three parameters control the action:
| Name | Type | Mandatory? |
|---|---|---|
| Target class | List the instantiated classes of objects that may be linked to an IP address | Yes |
| Functional CI | List the CIs of class defined by Target class which an IP address can be allocated to | Yes |
| IP Attribute | IP attribute of the CI that the IP should be allocate to | Yes |
These parameters are automatically computed and may differ from one data model to another. For instance, a server may have only one IP address (it's management IP, like in the standard data model) or multiple ones (a management and a backup IP). Once the parameters are set and the Apply button is pressed, TeemIp confirms the operation and displays the details screen of the IP. The CIs tab should contain a pointer to the selected CI.
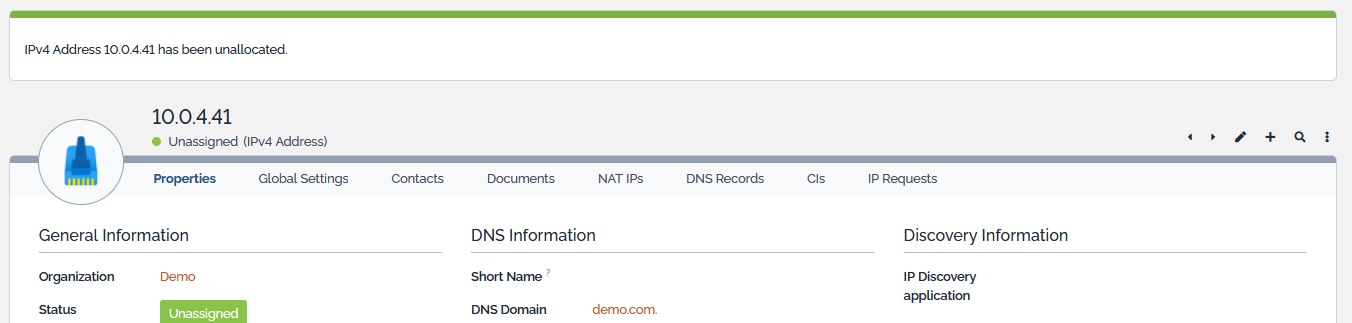
Un-allocate address from all CIs
This action simply un-allocate the IP from all CIs that it may be allocated to. This includes IP Interfaces. Action is launched as soon as the action is selected. A confirmation screen is then displayed.
Management of DNS RRS
Create / Update DNS RRs
This action will create the A / AAAA, PTR and CNAME DNS resource records that may be linked to the IP. A few criteria need to be met for this to happen:
- A zone corresponding to the IP's DNS Domain and belonging to the right DNS view must exist to create the A or AAAA records,
- A reverse zone corresponding to the IP must exist to create the PTR record,
- Each alias must belong to an existing zone in order to create a CNAME record.
Delete DNS RRs
This action will just delete all resource records linked to the IP.
Links between IP Addresses and CIs
TeemIp has been designed to provide a comprehensive modelization and documentation of the link(s) that a CI and an IP address may share together.
Some CIs, like servers or network devices, have one IP attribute that represents their management IP. For them:
- A unique IP can be attached to them,
- An IP address must be in the status Released or Unassigned to be attached to a CI,
- IPs that are in state Allocated cannot be set as IP attribute unless IP setting Allow attachment of already allocated IPs to CIs is set to Yes,
- Reserved IPs are… reserved,
- Once a CI is created or updated, the status of its attached IP is automatically changed to Allocated,
- If a Management IP is removed from the CI, its status becomes Released unless it is still linked to another CI.
Some others CIs, like IP interfaces attached to routers, may host several IP addresses. For them:
- One or more IPs (with no limitation of quantity) can be attached to them,
- An IP can be attached to them, regardless their status,
- Once an interface is created or updated, the status of its attached IPs is automatically changed to Allocated,
- If a link with an IP address is removed, status of IP moves back to Released unless it is still linked to another CI.
Impact of CIs' life cycle to IPs
Changes on CIs may have an impact on IPs. Here is what happens when…
- A Functional CI is created
- It is checked if the CI has IP Attributes,
- For each of these that do point to an IP:
- Status is set to allocated,
- Short name attribute is computed.
- A Functional CI is updated
- It is checked if the CI has IP Attributes,
- For each of these:
- Status of IP is updated if IP has changed (new IP is set to allocated and previous one is set to released),
- Short name is changed if the CI name has changed.
- A Functional CI is deleted
- It is checked if the CI had IP Attributes,
- For each of these that do point to an IP:
- Status is set to released,
- Short name attribute is reset to empty string.
- A functional CI becomes obsolete
- Its IPs may automatically be released from it, if IP Setting Release IPs from CIs that become obsolete is set.
Releasing IPs
When an IP is set to the status “Released”, it is removed from all CIs and all interfaces if IP Setting Detach released IPs from CIs is set to Yes (which is the default setting).
Automation
When linking an IP together with a CI, one must insure that both the CI's and the IP's status are consistent. TeemIp may automatically and periodically check the status of IPs and their coherency with the CIs they are attached to, if any. This behaviour is driven by a set of parameters defined in Global IP Settings. For any given organization, should the configuration parameter… :
- Allocate IPs attached to production CIs (*) be set to Yes, TeemIp will make sure that IPs attached to CIs are “Allocated”.
- Release IPs from CIs that become obsolete (*) be set to Yes, TeemIp will release all IPs that are still allocated to obsolete CIs,
- Un-allocate IPs that are not attached to a CI (*) be set to Yes, TeemIp will unassign the IPs that are not attached to a CI,
- Release IPs from subnets that are released be set to Yes, TeemIp will release all IPs that belong to released subnets,
- Allow attachment of already allocated IPs to CIs be set to Yes, TeemIp will allow, from the CI details screen, the attachment of an allocated IP to a CI.
- Detach released IPs from CIs be set to Yes, TeemIp will detach IPs which status moves to “Released” from all CIs. This does not include interfaces for which released IPs are always detached.
The 3 first actions (*) are handled by background tasks which default parameters can be overwritten in the configuration file.
'teemip-ip-mgmt' => array (
...
'ip_allocate_on_ci_status' => array (
'enabled' => true,
'debug' => true,
'periodicity' => 3600,
'status_list' => array (
0 => 'implementation',
1 => 'production',
),
),
'ip_release_on_ci_status' => array (
'enabled' => true,
'debug' => true,
'periodicity' => 3600,
'status_list' => array (
0 => 'obsolete',
),
),
'ip_unassign_on_no_ci' => array (
'enabled' => true,
'debug' => true,
'periodicity' => 3600,
'target_status' => 'unassigned',
),
...
),
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| enabled | Enable or disable the function |
| debug | Add verbosity to the process |
| periodicity | Periodicity of the background task |
| status_list | List of status that trigger the action |
| target_status | Status of the IP once the action is done |
Please, refer to the Configuration File chapter for further details.